Principal Gaussian Overbound for Heavy-tailed Error Bounding
Published in IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024
We present a novel approach to overbounding heavy-tailed error distributions by leveraging the Gaussian mixture model. Specifically, we employ the bimodal Gaussian mixture model (BGMM) and utilize the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm to accurately fit the error distribution. The membership weights of the BGMM are analyzed, and the membership weight of the tail component is proved to be a convex function of the error. Then, we introduce a partitioning strategy based on the convex property of the tail component’s membership weight, which effectively divides the BGMM into the core and tail regions. In each region, one of the Gaussian components of the BGMM holds a dominant position, and a CDF overbound is constructed based on the inflation and shifting of the dominant Gaussian component. The proposed overbound is proved to be an unimodal and symmetric distribution, which indicates that its overbound property can be preserved through convolution.
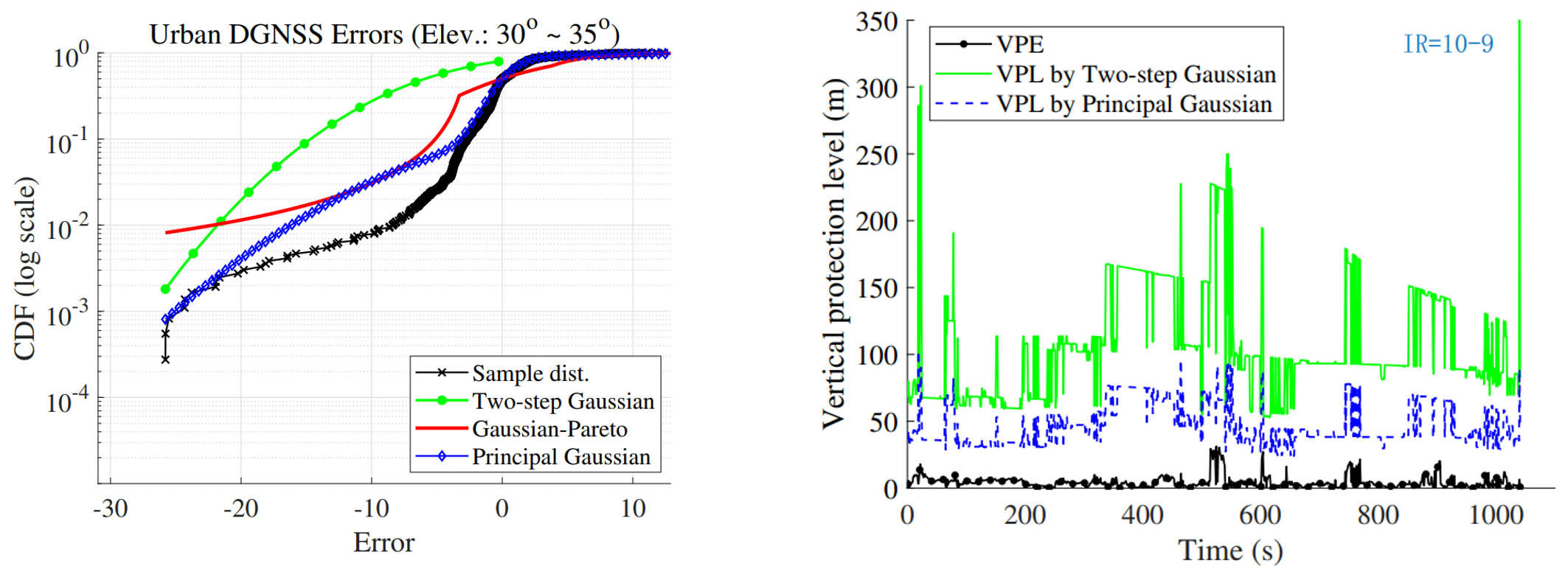
(a) The CDF (in logarithm scale) of the proposed method (Principal Gaussian overbound), the two-step Gaussian overbound, Gaussian-Pareto overbound for Urban DGNSS errors (heavy-tailed distribution); (b) The protection level of LS solution based on the proposed method (Principal Gaussian overbound) and the two-step Gaussian overbound when integrity risk is set as 10^-9.
The bounding performance of the proposed overbounding method is evaluated on the Differential Global Navigation Satellite System (DGNSS) pseudorange data, which is collected from a slightly urbanized area in Hong Kong. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method produces a shaper bound on heavy-tailed error distributions compared to the Gaussian overbound realized by the two-step method. Furthermore, it exhibits competitive bounding performance when compared to the Gaussian-Pareto overbound. In the position domain bounding, the mean vertical protection level (VPL) is reduced by over 50% in comparison to the two-step Gaussian overbounding method. The contributions of this study are two folds: 1) proposed a comprehensive method to determine the CDF overbound for the heavy-tailed error distribution based on the Gaussian mixture model (GMM), where a thorough analysis of the membership weight of the GMM is conducted, and severed as the theoretical foundation for constructing the overbound; 2) proved that the overbound property of the proposed method can be preserved through convolution, making it possible to calculate the protection levels in the position domain and facilitating the applications in integrity monitoring research.
Recommended citation: Yan, P., Zhong, Y., & Hsu, L. T. (2024). "Principal Gaussian Overbound for Heavy-tailed Error Bounding". IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 61(1), 829-852, http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TAES.2024.3448405
Download Paper | Download Slides
