Jackknife test for faulty GNSS measurements detection under non-Gaussian noises
Published in ION GNSS+ 2024, 2024
Fault detection is crucial to ensure the reliability of navigation systems. However, mainstream fault detection methods are developed based on Gaussian noise assumptions, while other methods targeting non-Gaussian noises lack rigorous statistical properties. The performance and reliability of these methods are challenged in real-world applications. This paper proposes a fault detection method for linearized pseudorange-based positioning systems under non-Gaussian noises. Specifically, this paper proposes a test statistic based on the jackknife technique, which is proved to be the linear combination of measurement noises without any assumption about noise distribution. Furthermore, a hypothesis test with the Bonferroni correction is constructed to detect potential faults in measurements. In a worldwide simulation, the proposed method demonstrates superior performance than the multiple hypothesis solution separation (MHSS) method under non-Gaussian noises. The reliability of the proposed method is further examined in detecting artificially injected faults for a differential global navigation satellite system (DGNSS) positioning system. Moreover, a real-world application to detect satellite clock anomalies for a single point positioning (SPP) system is investigated. The results show a significant improvement in reducing detection delay (8 minutes earlier than MHSS)
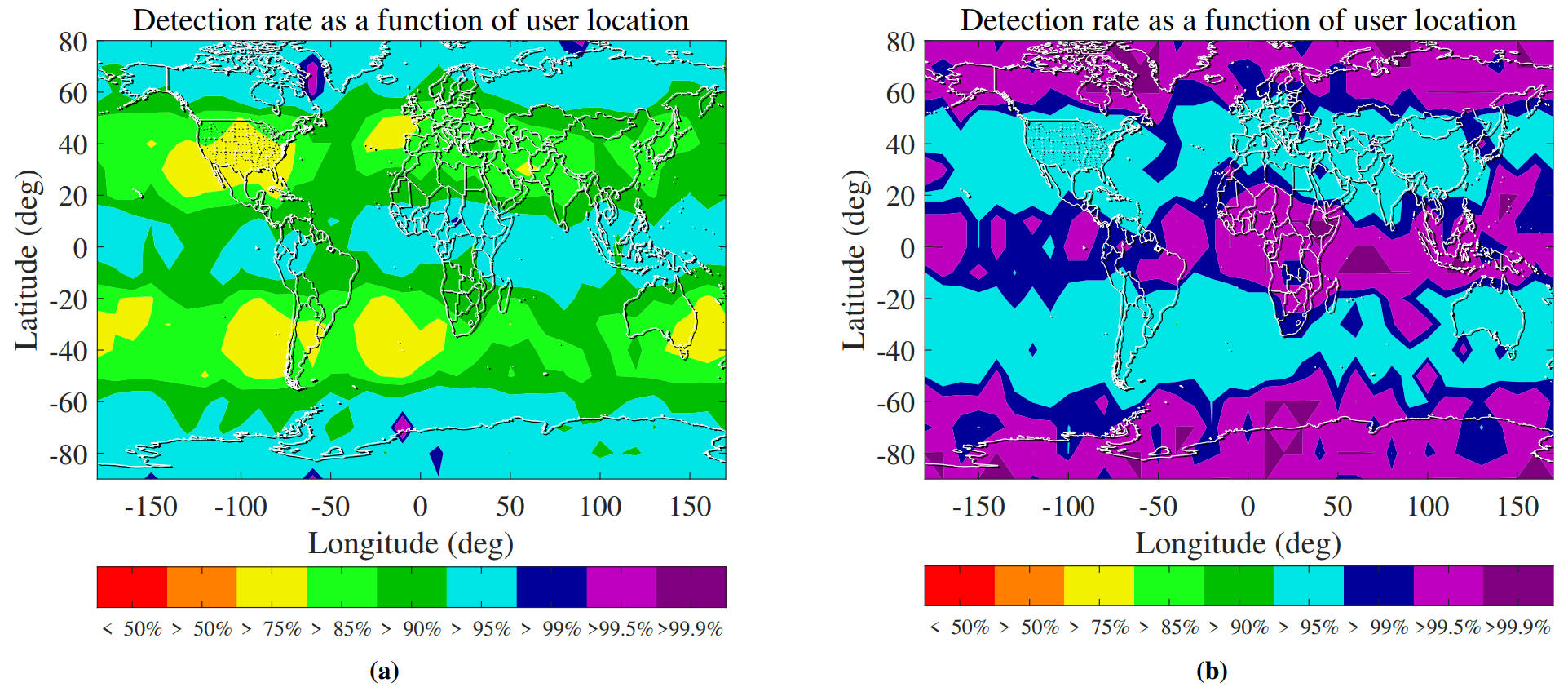 Contour plot of the detection rate of (a) the solution separation detector and (b) the proposed detector with non-Gaussian (Normal Inverse Gaussian) distributed nominal errors.
Contour plot of the detection rate of (a) the solution separation detector and (b) the proposed detector with non-Gaussian (Normal Inverse Gaussian) distributed nominal errors.
- Statues: Accepted by ION GNSS+ 2024 as the Student Paper Award
Recommended citation: Yan, P. (2024). "Jackknife test for faulty GNSS measurements detection under non-Gaussian noises". In ION GNSS+ 2024 (pp. 1619-1641), https://doi.org/10.33012/2024.19837
Download Paper | Download Slides
