A Fault Detection Algorithm for LiDAR/IMU Integrated Localization Systems with Non-Gaussian Noises
Published in International Technical Meeting 2024, 2024
Fault detection for localization systems with non-Gaussian measurement noises is a challenging task. This paper investigates the impacts of noise modeling on fault detection performance in the inertial measurement units (IMU) and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) integrated localization system based on the extended Kalman filter (EKF). Specifically, we model the noise distribution of LiDAR range measurements as a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) and establish a clear relationship between the measurement noise and the measurement residual in EKF through error propagation. After proving that the measurement residual is also GMM distributed, a test statistic is constructed by transforming the measurement residual to a variable that approximates a standard multivariate normal (MVN) distribution based on the law of total covariance. Then, a Chi-squared test is performed based on the constructed test statistic to detect potential faults. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated in the simulated environment regarding two types of measurement failures, including the step failure and the slope failure. Compared to the method that adopts Gaussian noise modeling, the proposed method demonstrates its superiority in detecting small faults and the improved sensitivity to slowly increasing faults.
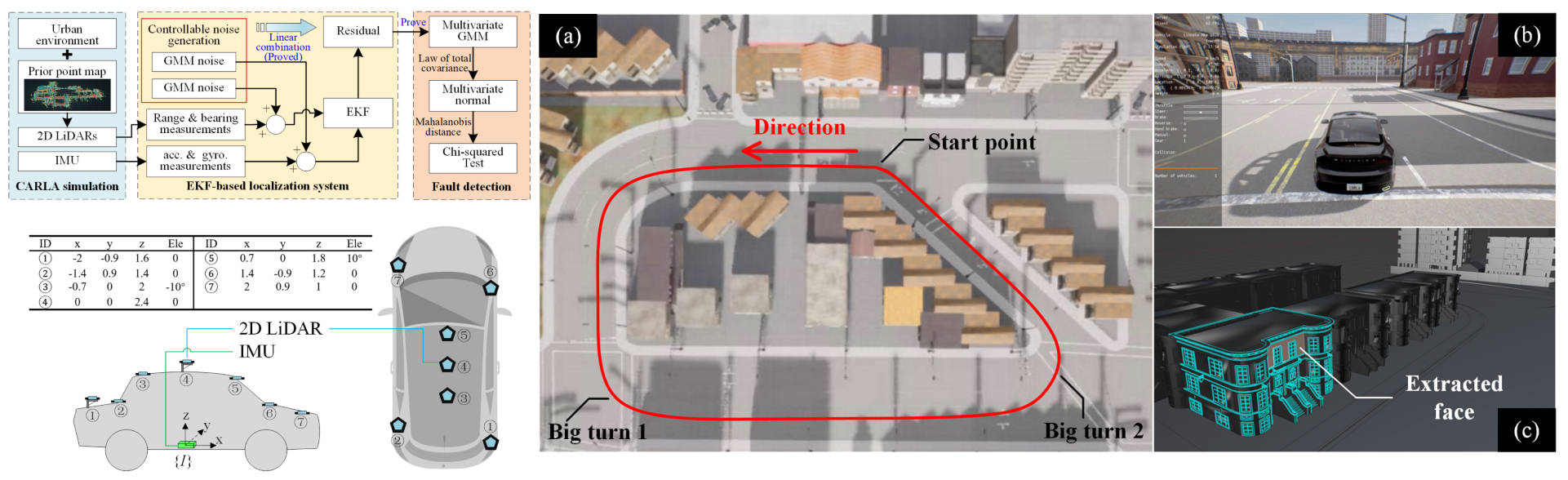 The architecture of the proposed method and the simulated environment where we apply the algorithm.
The architecture of the proposed method and the simulated environment where we apply the algorithm.
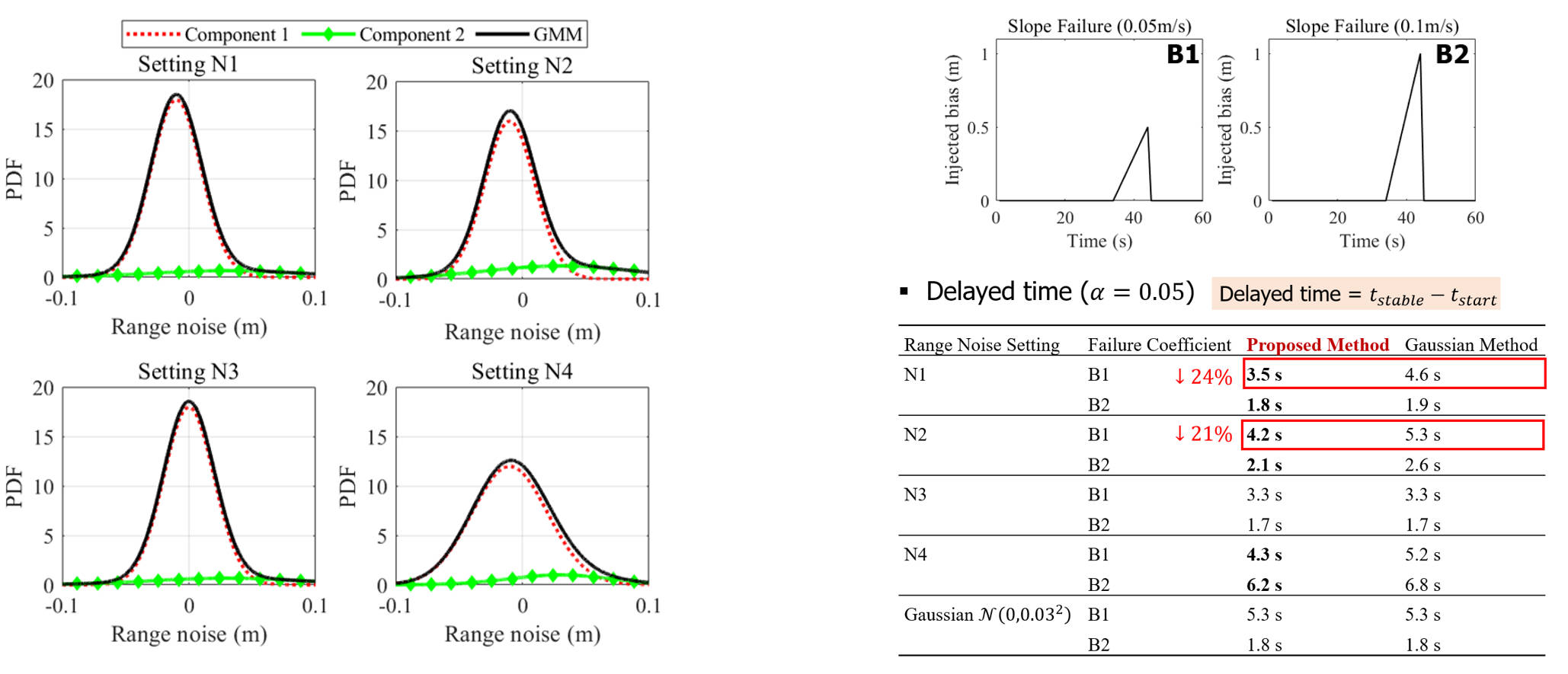 Four non-Gaussian noise settings, two types of slope failure settings, and comparison of the proposed method and the Gaussian method in terms of delayed time.
Four non-Gaussian noise settings, two types of slope failure settings, and comparison of the proposed method and the Gaussian method in terms of delayed time.
Recommended citation: Yan, P., Wen, W., Huang, F., & Hsu, L. T. (2024). "A Fault Detection Algorithm for LiDAR/IMU Integrated Localization Systems with Non-Gaussian Noises". In Proceedings of the 2024 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation (pp. 561-574).
Download Paper | Download Slides
