Multiple Faults Isolation For Multi-Constellation GNSS Positioning through Incremental Expansion of Consistent Measurements
Published in IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024
We propose an expanding approach to detect and isolate multiple faulty measurements in pseudorange-based positioning systems. Specifically, the proposed algorithm starts with constructing a minimum basic subset, which has the minimum studentized residual computed based on full set measurements. Then we incrementally expand the basic subset with no-fault hypothesis testing by examining the ordered jackknife residual. The proposed method is evaluated in a simulated experiment to isolate multiple faults for a set of users distributed over the world during one day. In the setting of six simultaneous injected faults with the magnitude uniformly distributed in [10 m, 20 m], the proposed method exhibits a remarkable 50 % reduction in the mean swamping event rate (healthy measurements are wrong excluded) and 38% reduction in the mean post-isolation positioning error, compared to the deletion-based greedy search method (Blanch, Walker, & Enge, 2015).
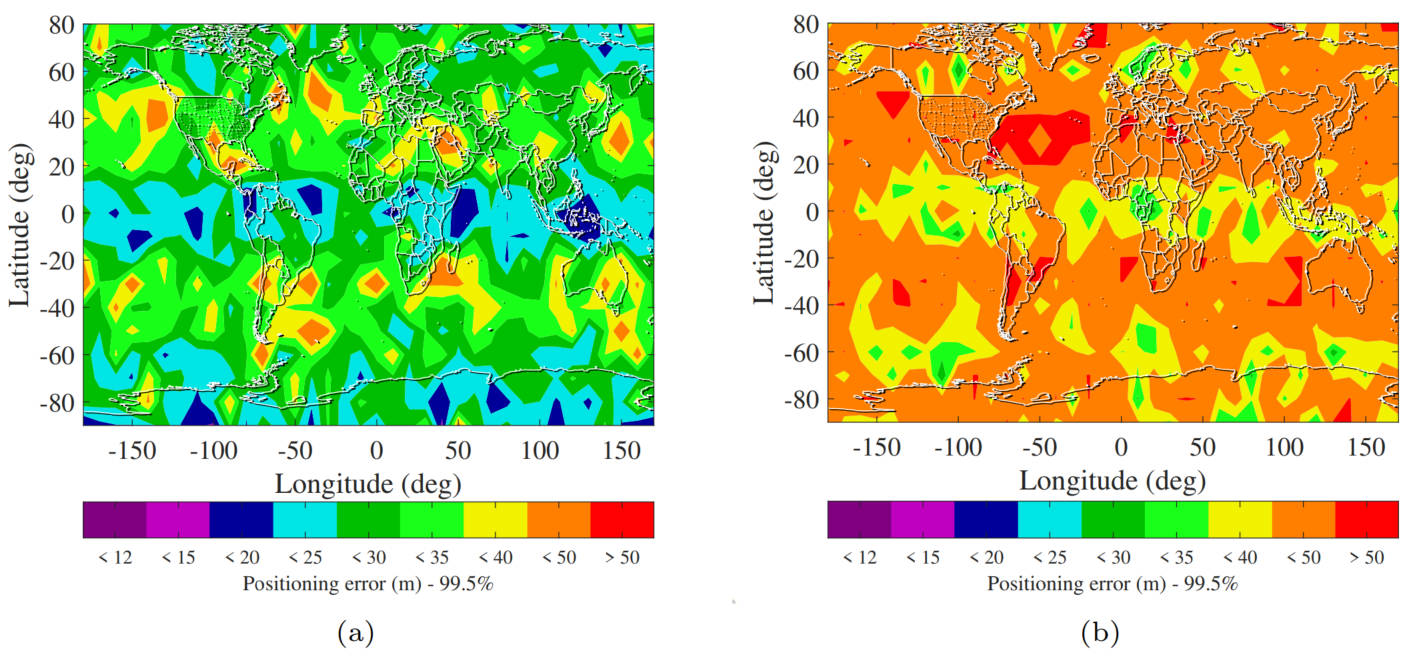
99.5% percentile of post-isolation positioning error over the course of the day by (a) the incrementally expanding algorithm and (b) the deletion-based greedy search algorithm in isolating multiple faults (six simultaneous faults, 20m, two constellation).
Recommended citation: Yan, P., Hu, Y., Wen, W., & Hsu, L. T. (2025). "Multiple Faults Isolation For Multi-Constellation GNSS Positioning through Incremental Expansion of Consistent Measurements". IEEE Sensors Journal, 25(4), https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2024.3524434
Download Paper | Download Slides
